How do precise motor programs generalize for robust behaviors?
Locomotor systems need the ability to maintain performance during a wide range of mechanical demands. Large fluctuations in body mass ...
Conduction of Signals in the Hawkmoth
The ability to quickly maneuver through a variety of environments requires a central nervous system that can rapidly transfer sensory ...
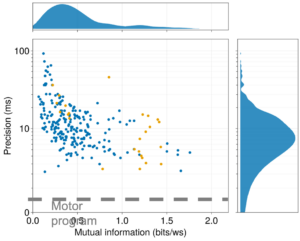
Origins of motor precision
Using information theory, we’ve seen that the flight motor program of moths such as Manduca sexta is temporally precise to ...
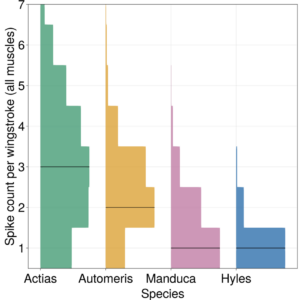
Flight motor programs across species: Are faster-flapping insects more precise?
Wingbeat frequency in flying insects spans several orders of magnitude; Even just in bombycoid moths, wingbeat frequency can vary from 5 Hz ...

Comparison of synchronous and asynchronous actuation strategies in response to perturbations
There are two regimes for actuating flapping wings known as synchronous and asynchronous. Synchronous flapping is where each wing beat ...
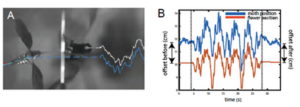
Fast Reference-Locking in Hover Feeding Hawkmoths
Tracking and stabilization involves control around a fixed point. Depending on the method of control, this may or may not ...

Performance advantages of centralized neuromechanical control over variable terrain
Centralization which measures the coupling between neuromechanical modules that mediate responses to perturbations, has been determined to be an important ...
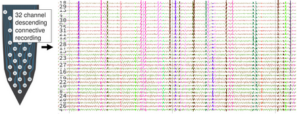
Task-Relevant Descending Information in the Neck Connective
The neck connective in insects connects the brain to the thoracic motor control centers. This is a bottleneck in information-flow, ...

Variation of Centralization with Terrain Complexity and Locomotion Speed
Locomotion emerges due to interactions between various subsystems such as sensory systems for vision. Rather than analyzing all the subsystems ...
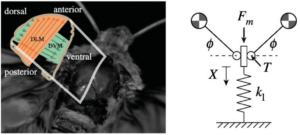
Do insects flap at their resonant frequency?
Centimeter-scale flapping flight is an extremely power-intensive way to get around, because it requires powerful, muscle-driven movement at high frequencies ...
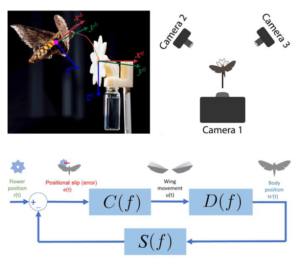
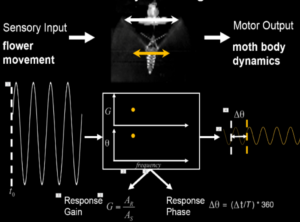
What underlies the emergent agility of hawkmoth flower tracking
One aspect of flight agility of hawkmoth M. sexta is that it sustains long bouts of hovering mid-air while feeding ...

Determining the biochemical changes associated with feeding and flight
Animals are driven to move, seek food resources, or find mates based upon their physiological needs at a given time ...
Temporal encoding across a motor program for the hawkmoth’s agile flight
Animals perform a plethora of robust, agile movements in natural environments by actuating and coordinating many muscles. However, the nervous ...
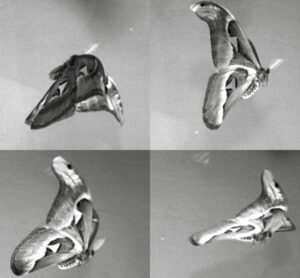
within-wingstroke body motion affect on insect flight dynamics
Current quasi-steady models of insect flight often prescribe constant body dynamics during a wingstroke. However, many silkmoths and butterflies experience ...

The evolution of different strategies for agile flight
A wide diversity of wing shapes has evolved, but how is aerodynamic strategy coupled to morphological variation? Here we examine ...
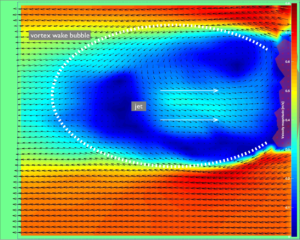
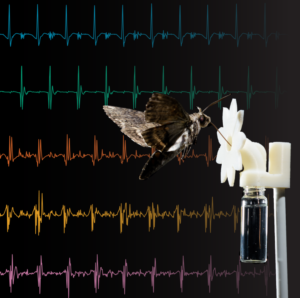
Natural flower wakes present aerodynamic challenges to pollinators
Plants and their pollinators must interact with changing airflow while simultaneously interacting as individual organisms. For flying pollinators, this includes ...
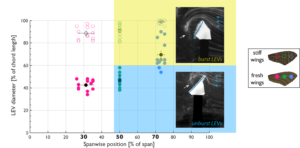
Natural wing flexibility prevents leading-edge vortex (LEV) bursting
The leading-edge vortex (LEV) is a well-known flight mechanism used by flapping insects, but the interplay between the bound LEV ...
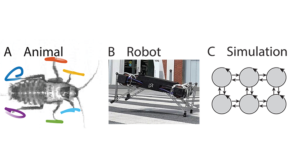
Centralization of Locomotor Control in Roaches & Robots
How do we assess the centralization of control in moving animals and machines and what are the consequences of changing ...
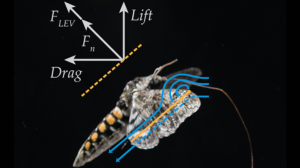
Moths change their behavior, but not their aerodynamics to feed in windy environments
How do moths maneuver in windy environments? Hawkmoths naturally hover and feed from flowers in nature. Insects have developed an ...

Moths slow their brains to track flowers in low light
Hawkmoths, like Manduca sexta, hover and track moving flowers during natural foraging in low light environments. Neural recordings from the ...
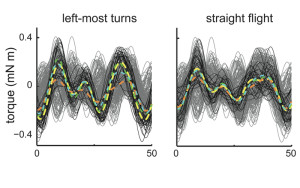
Simultaneous dimensionality reduction of motor commands and movement
Once a behaving organism has acquired, processed, and transmitted sensory information it must still alter patterns of motor activation in ...
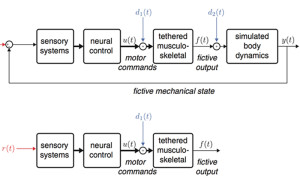
Control theoretic approaches to experiment and analysis of locomotion
Locomotion is an inherently closed-loop process. What that means is that when we move it changes how we perceive the ...
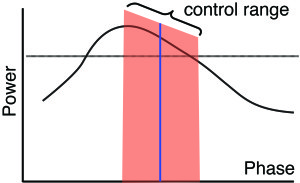
Precision phase control in flight muscles
The established perspective of flight control in insects holds that their remarkable maneuverability arises from neural modulation of relatively small ...
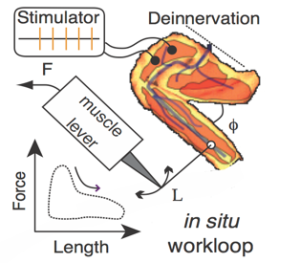
An intact-limb workloop reveals how cockroach muscle changes function
In the previous project we altered the commands the cockroach's brain was sending to its muscle in real-time while the ...
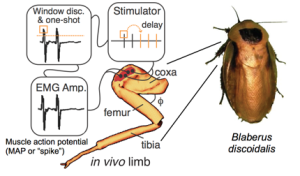
Rewriting motor commands in a freely running animal shows the multifunctionality of muscle
What is the potential of a particular muscle to control locomotion and how does mechanics affect the control consequences of ...
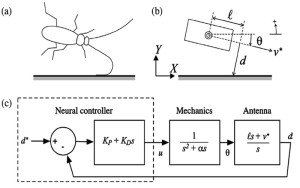
Bio-inspiration from how cockroaches navigate by touch
Animals must sense their environment in order to navigate. American cockroaches (Periplaneta americana L.) in the natural world often face ...

How roaches run on rough terrian.
We tested whether mechanical stabilization strategies without external sensing can yield successful locomotion in a challenging environment. In this study, ...