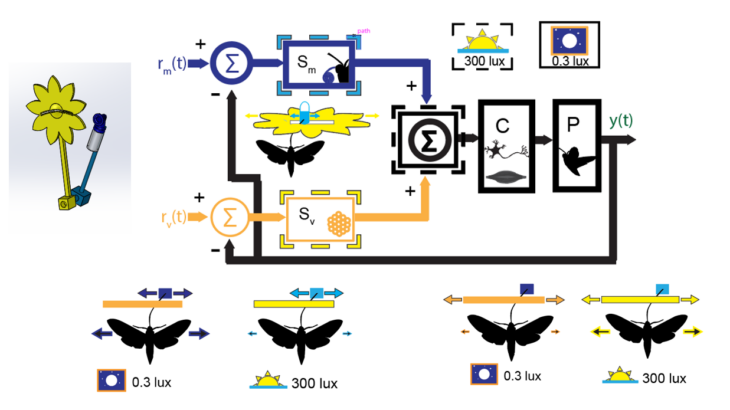
Multisensory Integration is Luminance-Dependent
Hawkmoths such as Manduca sexta use proboscis mechanosensation as well as vision to track moving flowers while hover-feeding. In crepuscular ...
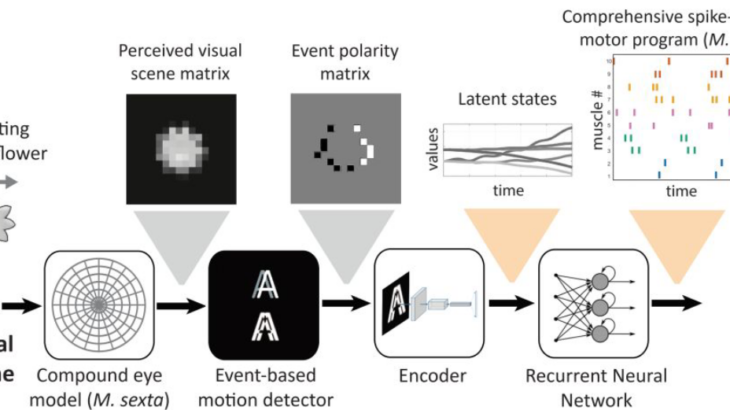
A sensorimotor system model to predict sensory-modulated motor program that is temporally precise, coordinated and comprehensive
Animal locomotion poses many challenges to an animal’s sensorimotor processing, especially for goal-directed tasks in dynamic and uncertain environments. To ...
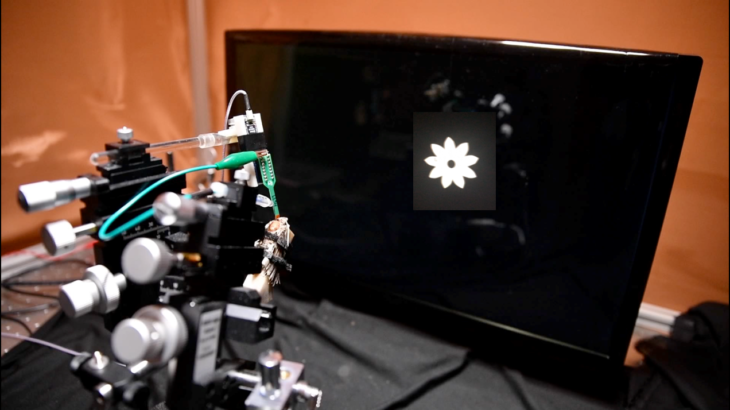
How an ecologically-relevant odor affects visual motion processing
The function of a visual system is to condense and transform patterns of light into a form that is meaningful ...
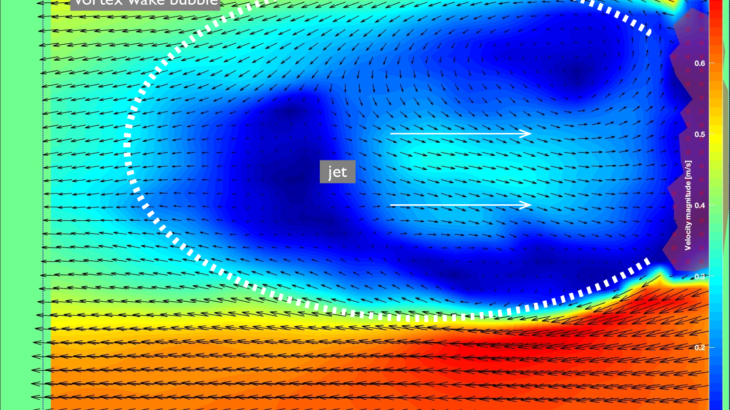
Natural flower wakes present aerodynamic challenges to pollinators
Plants and their pollinators must interact with changing airflow while simultaneously interacting as individual organisms. For flying pollinators, this includes ...
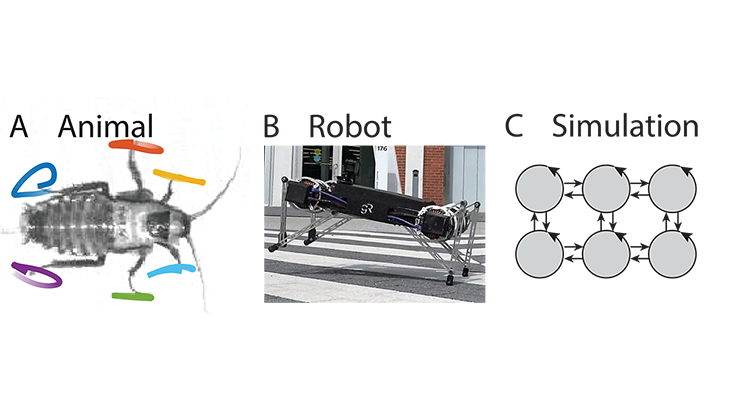
Centralization of Locomotor Control in Roaches & Robots
How do we assess the centralization of control in moving animals and machines and what are the consequences of changing ...

Moths slow their brains to track flowers in low light
Hawkmoths, like Manduca sexta, hover and track moving flowers during natural foraging in low light environments. Neural recordings from the ...
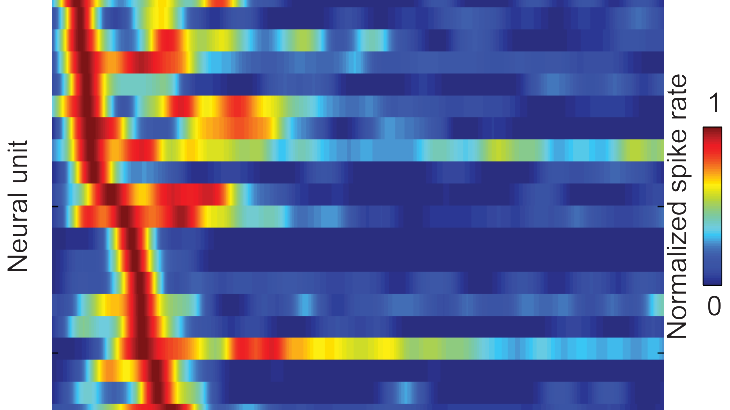
How antennae encode mechanical stimuli for tactile navigation
In an earlier research project with Dr. Jean-Michel Mongeau (now professor at PSU) we looked at the how cockroaches use ...
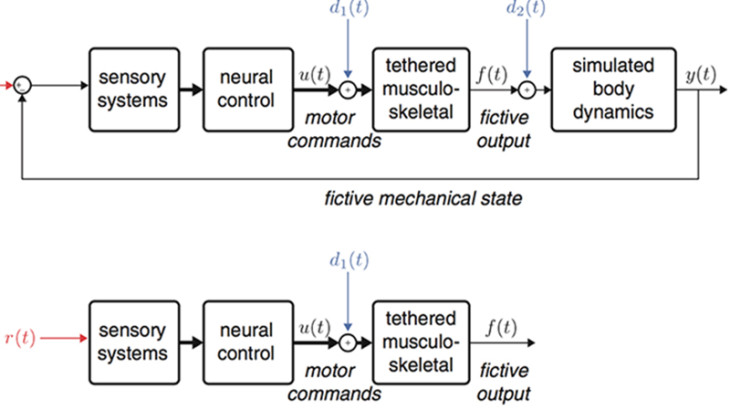
Control theoretic approaches to experiment and analysis of locomotion
Locomotion is an inherently closed-loop process. What that means is that when we move it changes how we perceive the ...
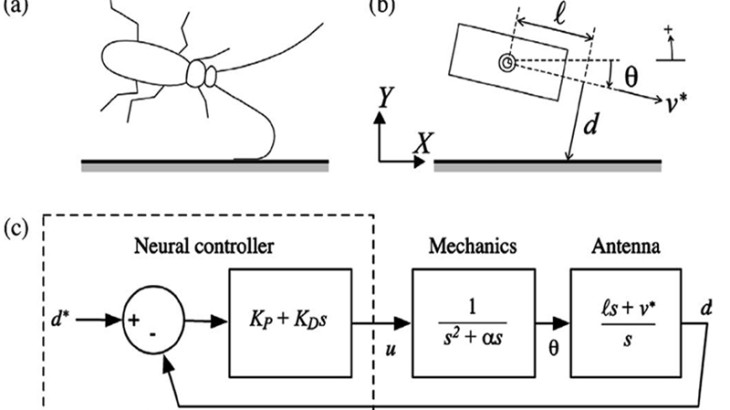
Bio-inspiration from how cockroaches navigate by touch
Animals must sense their environment in order to navigate. American cockroaches (Periplaneta americana L.) in the natural world often face ...