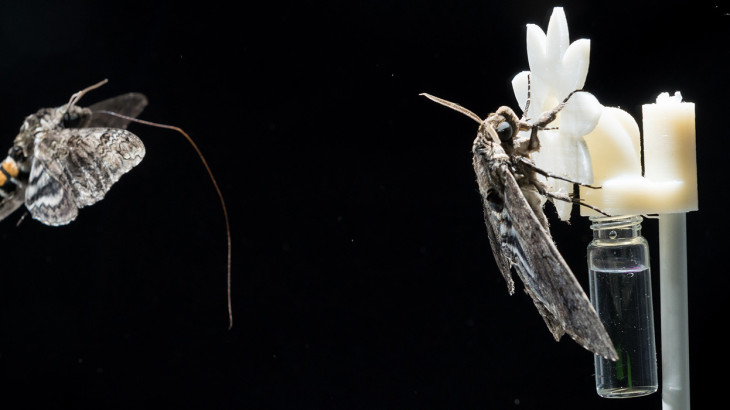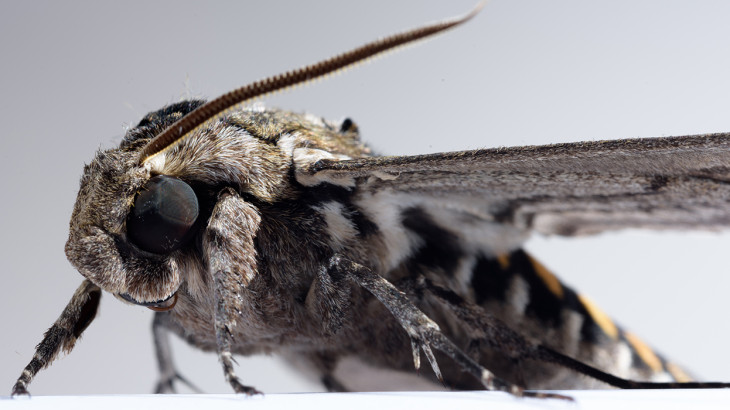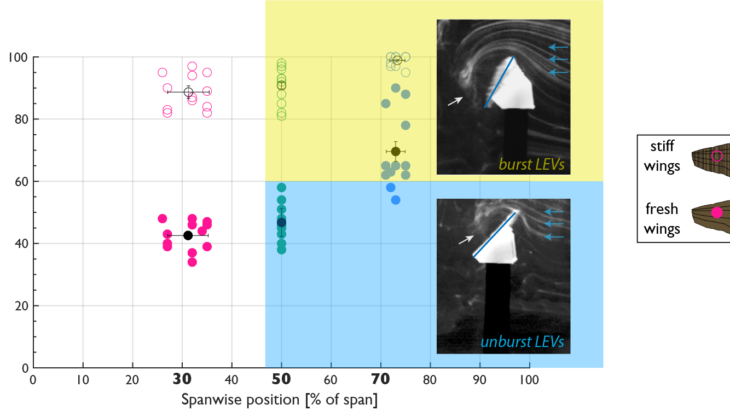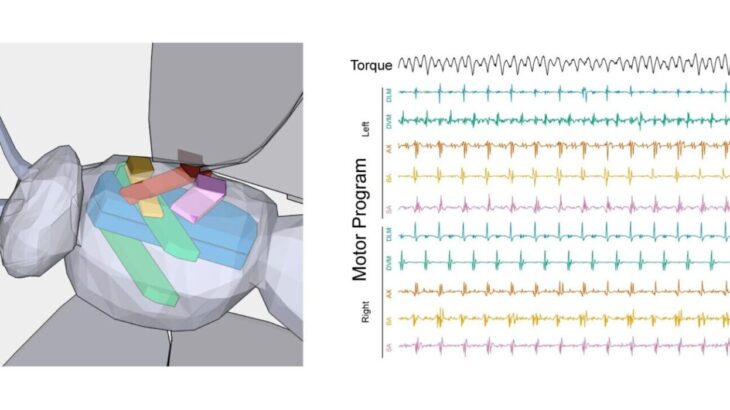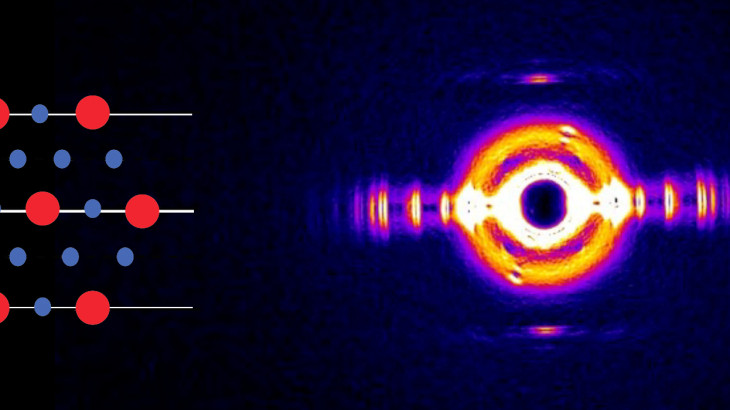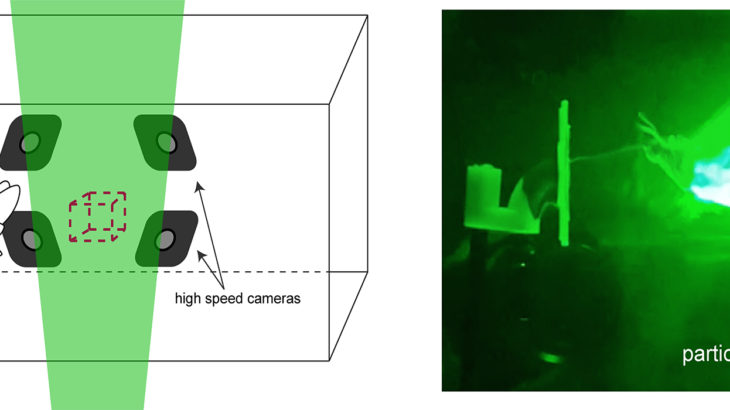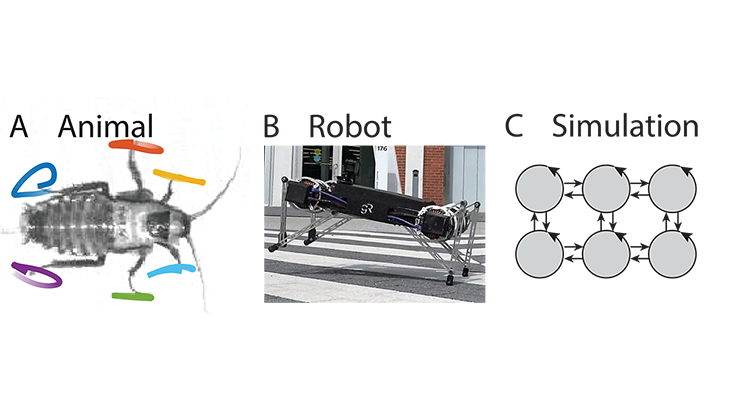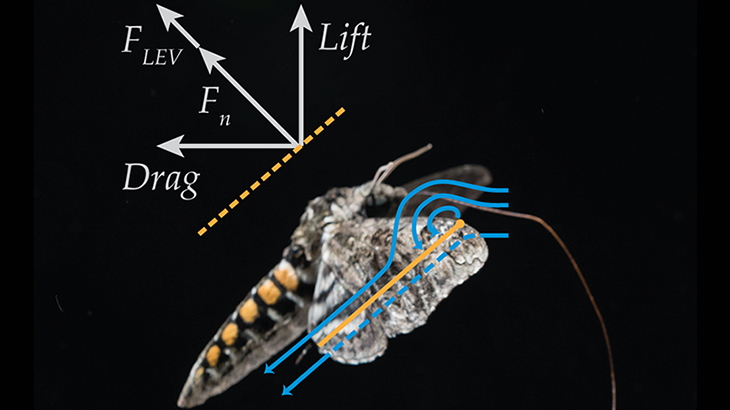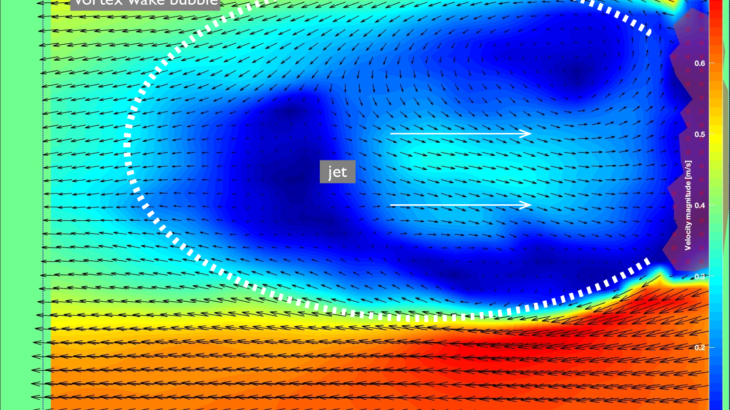
Plants and their pollinators must interact with changing airflow while simultaneously interacting as individual organisms. For flying pollinators, this includes flight through gusts and performing complex aerial maneuvers. Recent studies have begun to explore how these animals alter behavior in response to unsteady air, but we do not know if these conditions represent the local […]