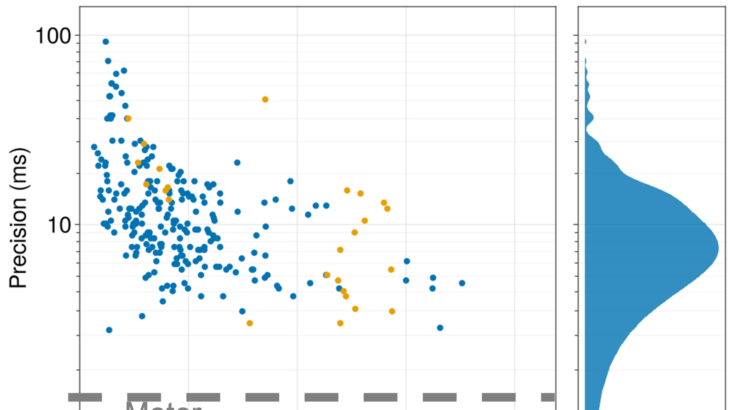
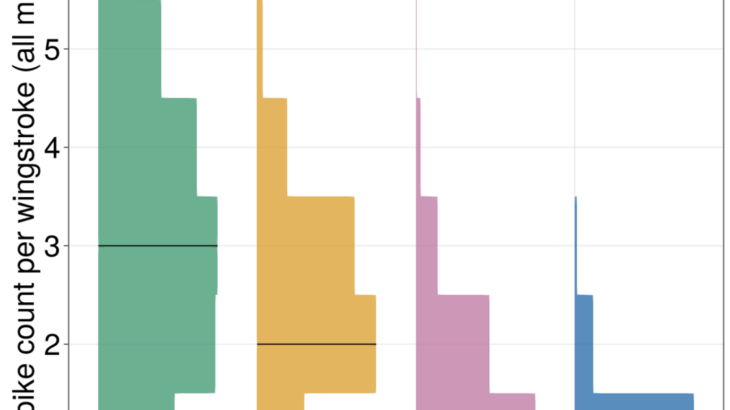
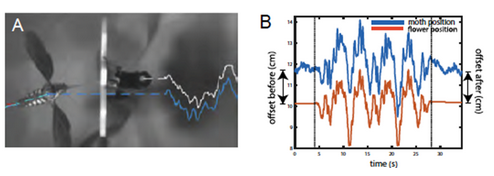
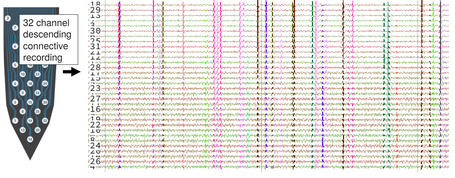
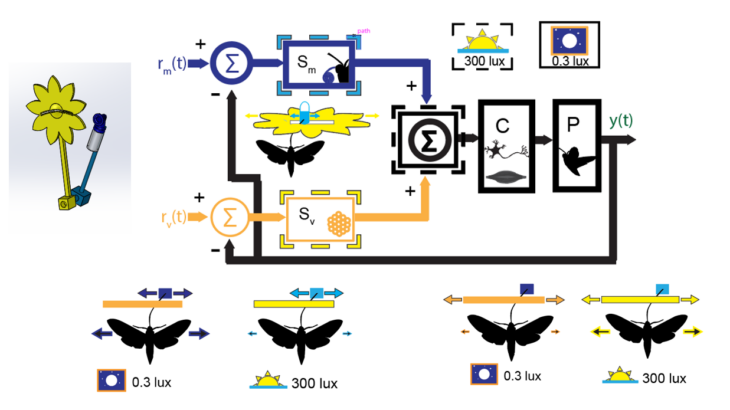
Locomotor systems need the ability to maintain performance during a wide range of mechanical demands. Large fluctuations in body mass due to growth, injury, or feeding prove to be an important example of such demands. Foraging Manduca sexta can increase their body mass by approximately 50% in a short period of hovering feeding while still […]